Digital Image Processing
| Course: | GIS 4307 Digital Image Processing |
| Credits: | 4 |
| Instructor: |
Geography Department
College of Liberal Arts & Sciences |
Learn how Remote Sensing can be used to help study and address many global environmental issues around the world today and in the process gain a highly desirable job market skill set.
This course provides an introduction to the use of remotely sensed data in environmental research. Remote sensing is the science of acquiring data using techniques that do not require actual contact with the object or area being observed. The different sensors used to collect this information, and the interpretation techniques vary quite widely, and are being developed at an astounding rate. In this course, we will focus on the interpretation and applications of data from spaceborne imaging systems (eg: Landsat MSS, Landsat TM, Quickbird, MODIS, AVHRR and SPOT).
How is remotely sensed data used?
The number of disciplines that utilize remotely sensed data continues to increase. Geologists, geographers, climatologists, and ecologists have all adapted remote sensing techniques to their respective research. We will briefly discuss many different uses of remotely sensed data, but focus on natural resources management and ecological applications.

The advance of the Hubbard Glacier July 22, 2014, image from Landsat 8
Learn how we can use imagery to monitor change over time across our planet’s surface
Course Goals & Objectives
In this course you will learn about the fundamentals of Remote Sensing theory and technologies through the use of problem solving and spatial thinking skills. The approach used in this course is problem based learning applied to spatially explicit problems. These concepts are essential to the use of RS. You will develop your own analytical skills by addressing real-world problems within the spatial framework of RS. The specific objectives of this course are to:
- improve geographic problem solving abilities through the application of RS technology and knowledge and via the application of spatial thinking skills;
- learn geographic concepts and skills and determine their relevance to you;
- sharpen critical thinking skills about geographic information, specifically in the form of remote sensing products – their reliability, accuracy and precision;
- acquire competency in basic knowledge and skills regarding RS.
What careers can I use these skills in?
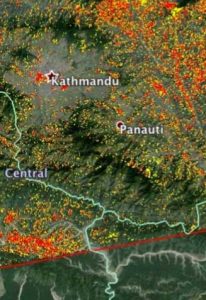
Natural Disaster Response
Learn how remote sensing aided the response to the Gorkha earthquake in Nepal on 5/25/2015.
This course in Digital Image Processing, often called Remote Sensing, will prepare you for jobs within this explicit field. Remote Sensing is used by image analysts for environmental consulting and in a wide variety of government jobs (e.g. USGS, EPA, NASA, CIA etc.). You will also gain skills applicable in a array of fields, such as environmental science, ecology, urban and regional planning, business, public health, and climatology.
For more information about some of the career opportunities associated with the skills you’ll learn in this course, check out this article from Science Magazine: Careers in Geoscience and Remote Sensing.
Course Format
The format of this course will involve weekly readings and videos with associated assignments, focused on fundamental topics and theory. Weekly activities will also be assigned based on interactive assignments, feedback and other learning activities. Laboratory sessions are designed to provide hands-on experience in the processing and interpretation of remotely sensed information. The weekly labs are a significant portion of the course and do take a good deal of time and patience to work through – but these make up the backbone of this class and this is why this is a 4 credit hour course. This is where you will apply the fundamentals of what you have leant about remote sensing to the practicalities of undertaking these analyses. The hands on labs are the critical piece of this course and this is what allows you to market yourself as an image analyst, with hand-on experience, and a sample project/portfolio of work.
The course will be composed of 10 modules:
- Introduction To Remote Sensing (RS)
- Remote Sensing Data Collection
- Computing Requirements, Image Quality And Display
- Image Correction
- Image Enhancement
- Image Classification
- Continued With Classifiers, Change Detection & Advanced Analyses
- Hyperspectral Analysis
- Google And Getting Imagery
- Time Series Analysis Of Imagery
Please note: the Labs are time consuming. You will need to spend a lot of time, on the computer working on the labs to complete these weekly assignments. I do not want this to be a shock to anyone and so here is your heads up – learning RS takes a lot of time and patience – but is an amazing tool once you have it, so hang in there! It is a wonderful and highly marketable skill.
Image source: http://flic.kr/p/7HeQTC

